Tarps, Covers & Liners. Industrial Textile Fabrication.
Marson Industries Australia Pty Ltd
Facts About Spill Containment Bunds

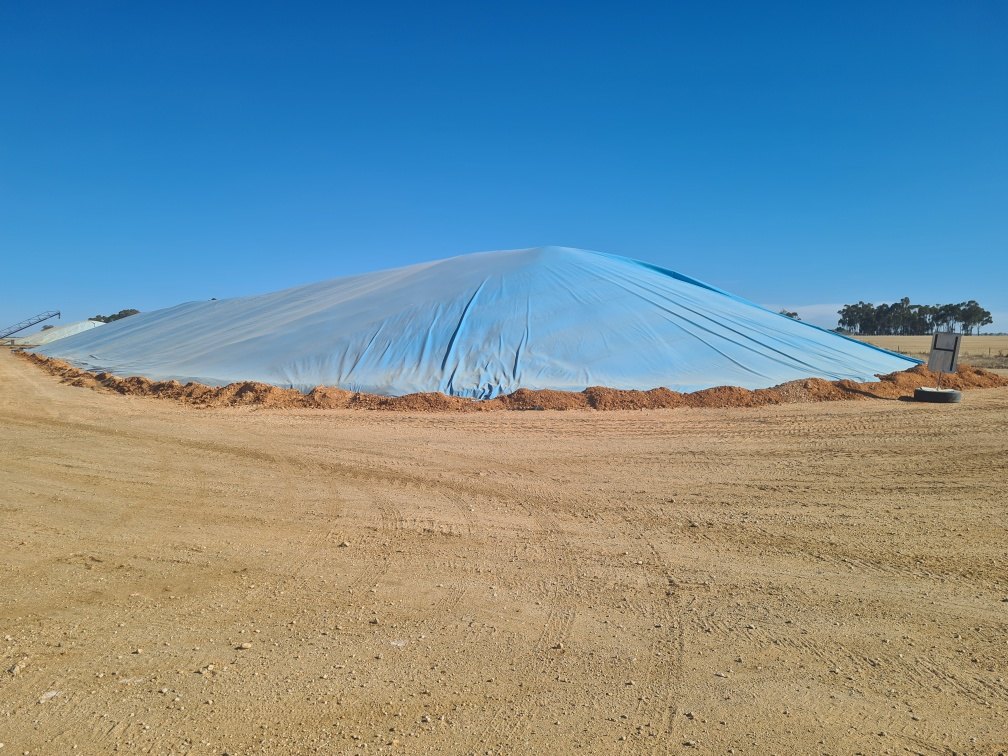
Spill management is something important and worth considering for the harmless handling, transportation and storage of containers, drums, equipment and tanks not only within a business premise but also outside. To familiarize with the facts about spill containment bunds, it is important to have a comprehensive understanding of what a bund is.
To begin with, a bund is a kind of brick wall or embankment or any other form of impervious material that forms the floor and perimeter of a given compound and offers a barrier for the retention of fluids. With the bund being the main section in a spill containment system, the entire system is simply referred to as a bund.
For safety purposes, it is important that bunds be designed to contain leaks and spillages of liquids that are processed, stored or used above the ground. In addition, bunds should also be designed so as to facilitate clean-up operations.
In addition to being used for the prevention of pollution in the receiving environment, bunds are also utilized for the purposes of fire protection, process isolation and product recovery.
The need for bunding systems should be established on site-to-site basis. There are numerous facilities that should have bunded areas. Some of these facilities include:
- Storage facilities for petroleum, pesticides or chemicals
- Electric transformers that contain oil
- Facilities that are used in the transfer of stored liquids
- Drum storage areas. These can either be permanent or temporary
- Processing areas
- Breweries, milk processing plants and wineries
- Facilities that are used to store substances other than water
Locations where spills are usually very common such as factories, workshops, transfer points, wash bays and service stations
Different kinds of facilities can have different kinds of bunds since the needs and design requirements may vary. The most common types of bunds are the square bund, the hump band and the ramp bund.
- Facts about Spill Containment Bunds- Design and Construction
During the designing and construction of spill containment bunds, there are certain rules that must be followed. This is in an effort to try and confer with the stipulated guidelines for bund construction. Here are some of the points that should be incorporated into the design of the bund.
- The Net Capacity
According to regulators, the net capacity of any bonded compound in a given storage facility should not be less than 120% of the largest tanks net capacity. It is important to take into account the capacity that is displaced by other types of tanks that are within the same bunded area. For purposes of bund design criteria, it is also important to treat all interconnected tanks as one with a total volume equivalent. In the case of flammable liquids, the capacity of the bund should not be less than 133% of the largest tanks capacity.
- Building Materials
The bunds walls and floor should be built with materials that are impervious to the contents of any container or tank that is within the bund. The material should be of sufficient structural integrity and strength to ensure that chances of leaking or bursting in ordinary use are minimal. In bund wall construction, it is not recommended that un-reinforced materials be used. In addition, the bunded area should be in a position to prevent the migration of any leakage or spillage to the adjacent environment. Not unless it is the only option available, earthen bunds are not recommended.
- Bund Height and the Tank Distance from the Wall
Wall-type bunds that are found in storage facilities should be between 0.5m and 1.5 meters high. This depends on the desired containment capacity and the bunds distance from the tank. The closer the tank is to the wall, the higher the wall should be. The distance between the bund and tank walls should not be less than one meter. If bunds walls are more than one meter above the compound floor, it is advisable to have step ladders to offer quick escape when the need arises. If vehicles are to access the bunded area, it is important to consider using ramps to maintain the effective bund height.
- Drainage
The bund floor should have a collection sump for easy removal of any accumulated liquids. In addition, the floor should be graded in a manner that the liquids collect in the floor sump. The sump should have no connections to sewer or stormwater drainage systems because it is just a collection point from which the liquid can be pumped out. The installation of drain valves should be done and all the pump controls should not be within the bunded area. Accumulated liquids from vessel raptures or spills can be easily collected and reused on the site. However, when it’s not appropriate or possible, an authorized liquid waste contractor should be asked to collect and dispose the liquid.
With these important designing facts about spill containment bunds, it is possible to construct a containment bund that can stand for decades.
Share this post